Lasse Schultebraucks IT Consultant
Efficient Full-Stack Application Development Using Spring Profiles
The development of full-stack applications often involves integrating various features, user roles, and user interfaces. In this context, the Spring Framework, in conjunction with Spring Boot, can offer a powerful solution. A crucial tool in the Spring arsenal is the use of “Profiles,” which allow configuring applications for different environments, thereby enhancing development efficiency. In this blog post, we’ll delve into Spring Profiles and explore how they can be used for developing a full-stack application using a specific scenario.
A Brief Introduction in Spring Profiles
Spring Profiles provide a means to manage application configurations based on environment variables, system properties, or other configuration sources. They allow defining different settings for different environments (e.g., development, production, testing) without altering the source code. This not only simplifies application deployment but also facilitates smooth local development.
The Scenario: Implementing a UserService Class with Spring Profiles
Imagine you’re developing a full-stack application that supports different user roles. Within this application, there exists a UserService class with a method named isAdmin(), which determines whether a user has administrative privileges. Depending on whether the user is an administrator or not, certain features and user interfaces are made accessible.
The challenge lies in creating a developer-friendly environment for working on admin functionalities without constantly switching between different user roles.
Solution: Utilizing Spring Profiles for Development
This is where Spring Profiles come into play. You can leverage Spring Profiles to override the UserService class and always set the isAdmin() method to true when the development profile (dev) is activated. This provides you with an easy way to work on admin functionalities within your local development environment.
Implementation:
1. Start by defining the UserService interface and a default implementation:
public interface UserService {
boolean isAdmin(User user);
}
@Service
public class DefaultUserService implements UserService {
@Override
public boolean isAdmin(User user) {
// Logic for checking admin rights
}
}
2. Create an alternative implementation for the UserService that is activated for the development profile:
@Profile("dev")
@Service
public class DevUserService implements UserService {
@Override
public boolean isAdmin(User user) {
return true; // Always true for admin in the dev profile
}
}
3. Active the Spring profile
Either Configure the Spring profile in your application.properties or application.yml file:
spring.profiles.active=dev
If you are using Intellij or another IDE which supports Spring, you can also activated your Spring profile in the run configurations:
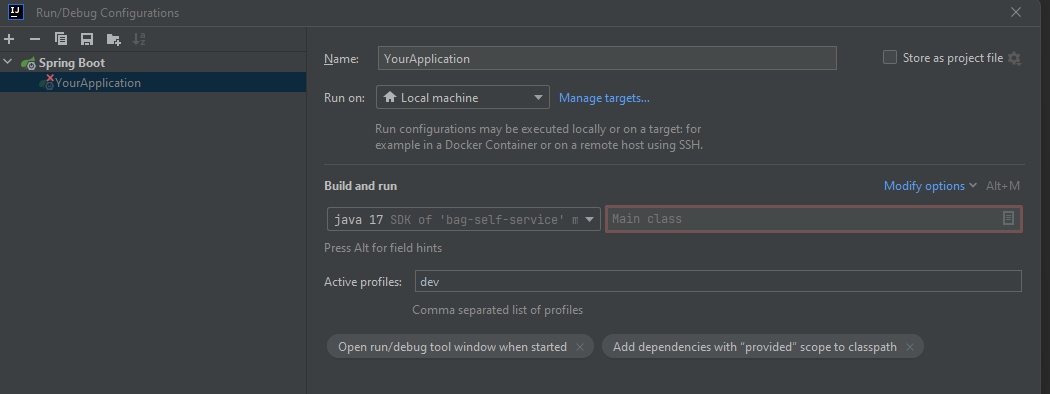
4. Use the UserService in your application:
@Controller
public class AdminController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@GetMapping("/admin/dashboard")
public String adminDashboard() {
if (userService.isAdmin(currentUser)) {
// Show admin dashboard
} else {
// Access denied
}
}
}
Conclusion
Checkout the official Spring Documentation to learn more about Profiles in Spring.
The utilization of Spring Profiles streamlines the development of full-stack applications. In the scenario described above, by leveraging profiles, you can override the UserService implementation, simplifying work on admin functionalities during development. This allows you to swiftly and seamlessly develop the desired features without compromising production logic. Spring Profiles thus provide an elegant solution for managing complex application scenarios and enhancing development efficiency.